Professional Software Quality Assurance Course (PSQA)
Professional Software Quality Assurance Course (PSQA)
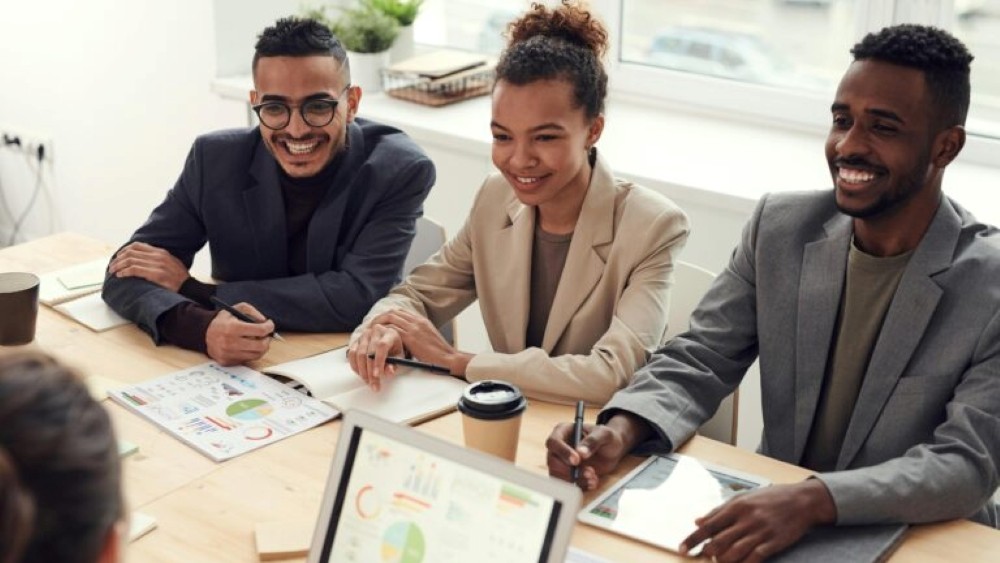
In today’s fast-paced IT industry, ensuring software quality is more critical than ever. The Professional Software Quality Assurance course equips you with the expertise to identify and resolve software issues efficiently, ensuring reliability, performance, and user satisfaction. With over 40% of software development costs attributed to fixing defects, strong QA skills are essential to reducing costs and improving software efficiency. This course covers core principles, best practices, and real-world applications, making it ideal for both aspiring and experienced QA professionals.
You will explore the entire software development lifecycle, learning how to implement testing strategies that minimize defects and enhance software quality. Master techniques such as functional, non-functional, and automated testing to ensure robust performance. Studies show that companies prioritizing QA experience a 20% reduction in post-release defects, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Upon completion, you will earn 18 PDUs, accepted by PMI-USA, strengthening your credentials and advancing your career in software quality assurance.
Course Details
Lecturer and Instructors
-Ms. Diana Arundathi Maddewithana Senior QA Engineer BSc in ITM - University of Moratuwa, MBA in MOT - University of Moratuwa
Batch Number & Starting Date
BATCH NUMBER 03 will be notified soon
Course Duration & Times
18 Hours (6 Weeks – 3 Hours per day) Every Saturdays From 6.00 pm to 9.00 pm
Eligibility Requirements
Anyone who is interested in Professional Software Quality Assurance can apply. Preferred IT, Computer Science, Engineering, or a related field.
Completed 2+
Batches
18 PMI – USA Accepted
contact hours
Internationally Valid
Certification
Benefits on having this course
Enhanced Career Opportunities:
Earning a PSQA certification boosts your credibility in the IT industry, opening doors to roles like QA analyst, test engineer, and quality assurance manager.
Increased Earning Potential:
QA professionals with specialized training are in high demand, leading to better job prospects, higher salaries, and more growth opportunities.
Strengthened Quality Assurance Skills:
The PSQA course provides a deep understanding of testing methodologies, defect management, automation tools, and best practices for delivering high-quality software.
Higher Software Delivery Standards:
Learn how to implement rigorous QA processes that minimize defects, enhance product performance, and improve customer satisfaction — making you an invaluable asset to any team.
Definition, importance, and goals of QA in software development.
Differentiating between quality assurance, quality control, and testing.
Overview of industry standards and models such as ISO, CMMI, and Six Sigma.
Responsibilities, skills, and mindset required for a successful QA career.
Phases of the software testing life cycle and their significance.
STLC in Waterfall Methodology: Requirements analysis, test planning, test case development, environment setup, test execution, test cycle closure.
STLC in Agile Scrum Methodology: Sprint planning, test execution within sprints, continuous feedback loops, integration of QA in daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
Manual Testing Techniques: Black-box testing, white-box testing, grey-box testing, exploratory testing.
Automated Testing Techniques: Unit testing, integration testing, system testing, regression testing
Test Planning: Objectives, scope, and criteria for success, resource planning and scheduling
Test Execution: Execution of test cases, logging results and tracking progress
Metrics-Based Reporting: Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics, test coverage, defect density, and test efficiency
Risk Management: Identifying and assessing risks, mitigation strategies and contingency planning.
Configuration Management: Version control, managing changes to the test environment.
Requirements for different types of testing environments
Configuration and maintenance
Creating and managing test data
Data privacy and security considerations
Identification, reporting, and classification of defects.
Prioritization and assignment.
Using Jira for defect tracking and management.
Integrating defect management with the development process.
Importance of API testing in modern applications.
Using tools like Postman
Writing and executing API test cases.
Automating API tests.
Introduction to Test Automation: Definition and Importance, advantages and benefits, types of tests suitable for automation.
Test Automation Tools and Frameworks: overview of popular test automation tools, introduction to test automation frameworks.
Test Automation Process: Test Script development, test execution and reporting, continuous integration and continuous testing.
Non-Functional Testing Overview: Definition and Scope, types of non-functional testing, importance of non-functional testing in software development lifecycle.
Integration of Test Automation and Non-Functional Testing: Best Practices for integrating test automation and non-functional testing, leveraging test automation for non-functional testing scenarios, challenges and considerations in combined test approach.

The PMP certification is highly regarded in the project management field and can enhance your career prospects. It demonstrates your knowledge and expertise in project management, increases your earning potential, and opens up opportunities for leadership roles in project management
The PMP course covers various aspects of project management, including project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and project closure. It also covers knowledge areas such as scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, risk management, and communication management.
The PMP course is suitable for professionals who are involved in project management or aspire to be project managers. It is ideal for project managers, team leaders, consultants, and individuals responsible for managing projects of various sizes and complexities.
To be eligible for the PMP course, you need to fulfill certain prerequisites set by PMI. You must have a secondary degree (high school diploma, associate’s degree, or global equivalent) with at least five years of project management experience, or a four-year degree (bachelor’s degree or global equivalent) with at least three years of project management experience.

